Field Key to Major Trees
Some leaf characteristics can vary depending on environmental conditions (light, temperature) and condition of the tree. Bark, bud, twig, fruit, and flower characteristics can also be diagnostic, but leaves are a good place to start. Many good guides exist, including those from which these drawings were taken:
- Trees of North America, CF Brockman & R Merrilees, Golden Press
- Eastern Trees, GA Petrides & J Wehr, Houghton Mifflin
View the PDF version of this page (Size: 18.2 MB)
Important Leaf Characteristics
- Arrangement on Twig:
- Dissection:
- Simple (no leaflets)
- Compound
- Pinnately
- Palmately
- Shape:
- Broad or narrow
- Symmetry
- Margins:
- Toothed or smooth
- Lobed
- Venation:
- Texture
- Pattern
- Texture:
- Thin or leathery
- Smooth or hairy
Arrangement on Twig:
Leaves (not leaflets) alternate
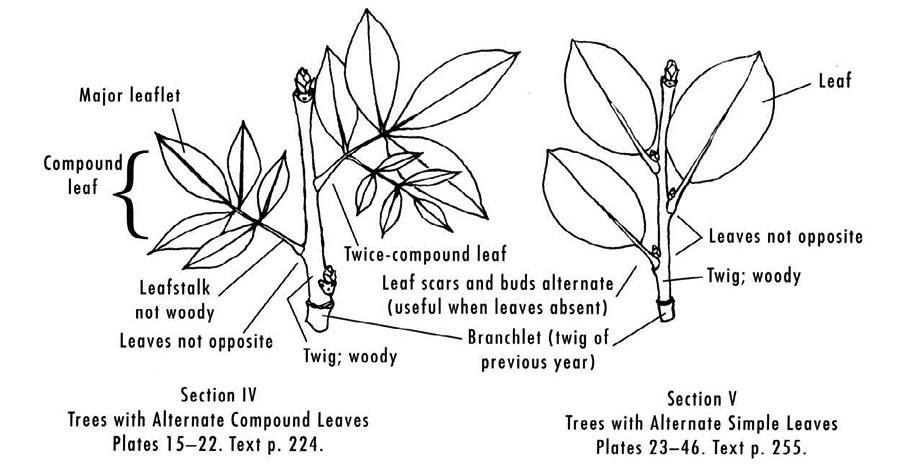
Simple Leaves, Untoothed (in shape categories)
Simple Shapes:
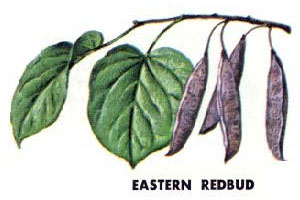
CC: Redbud (Cercis canadensis): heart-shaped, dark thin rough bark (purple flowers in spring)
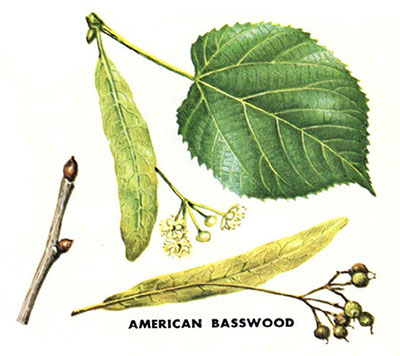
TA: Basswood (Tilia Americana): heart-shaped but toothed; lightly ridged bark, oval clumped trunks
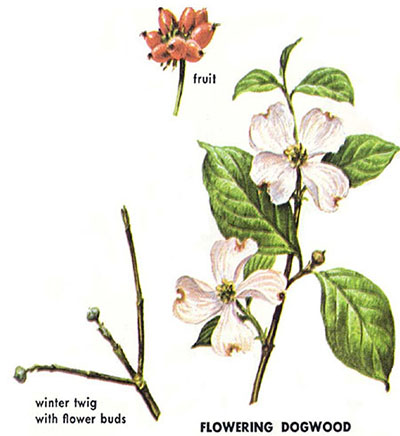
CF: Flowering Dogwood (Cornus florida): oblong, veins become parallel to edge; med. brown flaky bark

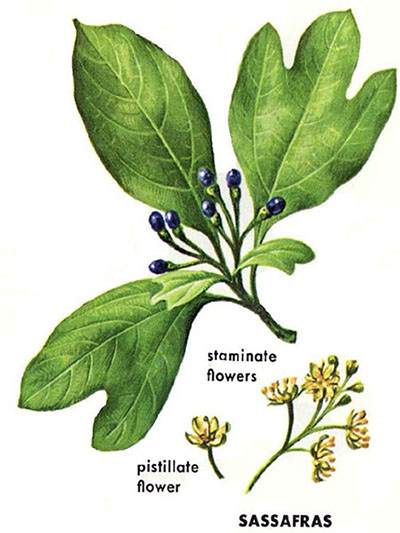
SA: Sassafras (Sassafras albidum): 1-3 rounded lobes ("mittens"); fragrant cinnamon brown twigs
Palmately lobed:
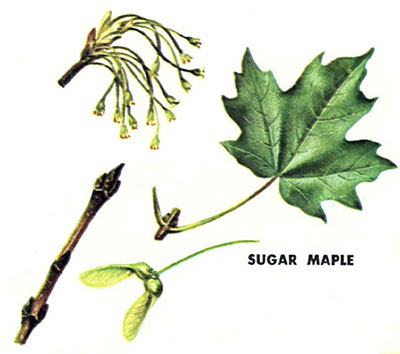
AS: Sugar maple (Acer saccharum): pointed lobes; mostly smooth gray bark
PO: Sycamore (Platanus occidentalis): large, pointed lobes; white, gray & green bark

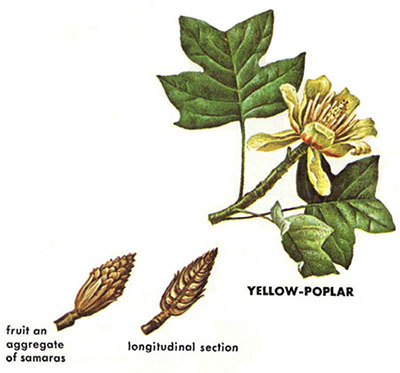
LT: Tulip Poplar (Liriodendron tulipifera): 3 squared-off lobes; straight ridged grayish bark
Pinnately lobed
Plated light bark (white oaks) or dark thick furrowed bark (black/red)
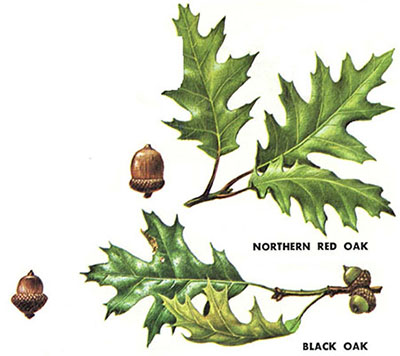
QR: Northern Red Oak (Quercus rubra): Thin smooth leaf, pointed shallow lobes; Dark bark with smooth streaks; smooth tight buds and acorn cap
QV: Black Oak (Quercus velutina): leathery, two-tone, hairy, deeper lobes; rough bark & acorn caps; "hairy" buds; yellowish underbark
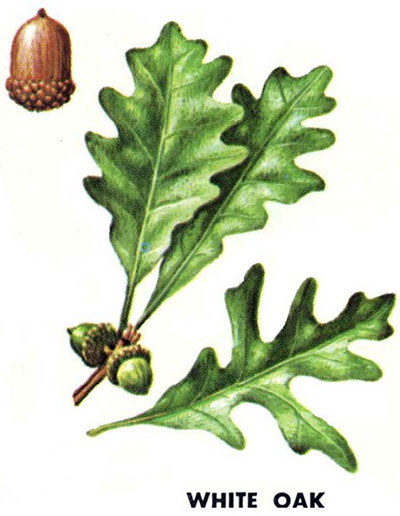
QA: White Oak (Quercus alba): rounded lobes, whitish plated bark

QM: Chinkapin Oak (Quercus muhlenbergii): wavy margins (rounded shallow lobes); whitish plated bark

Simple Leaves, Toothed
TA: Basswood (Tilia americana): [also above] heart-shaped, thin; furrowed light brown bark; often clumped
FG: Beech (Fagus grandifolia): thin pointed oblong, few coarse teeth; straight raised veins; smooth gray bark; icepick bud
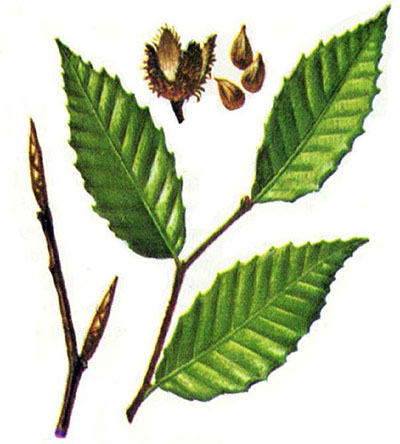
PS: Black Cherry (Prunus serotinal): pointed oblong, finely toothed, wavy margins, dark & shiny; dark thin plated bark with light horizontal lenticels (raised lines)

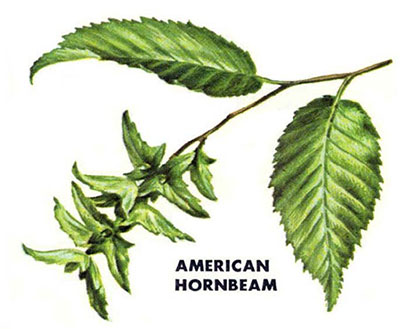
OV: Hophornbeam (Ironwood) (Ostrya virginiana): lance-shaped, double-toothed; loose shaggy bark; green buds
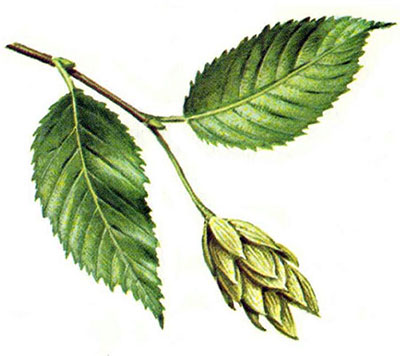
CR: American hornbeam (Carpinus caroliniana): Ironwood, Bluebeech, musclewood, lance-shaped, double-toothed; smooth gray sinewy bark; rusty brown buds
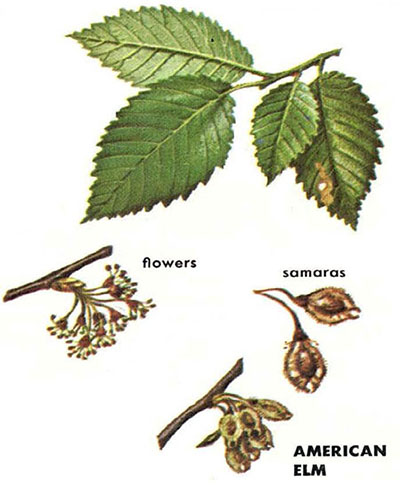
Elms: long-pointed oval larger at rounded, asymmetrical base, double-toothed, rough
UA: American Elm (Ulmus americana): thick corky bark with light layers; twigs & buds light brown, fuzzy
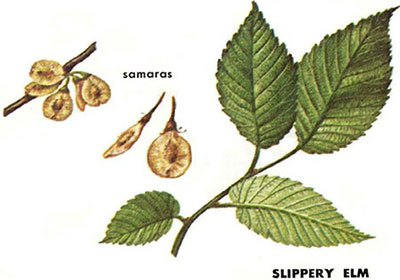
UF: Slippery Elm (Ulmus fulva): dark green and coarsely hairy below; thick bark without light layers, inner bark slippery; twigs and buds very hairy; buds very dark
CT: Hackberry (Celtis occidentalis): pointed oval, rounded base, thin, single-toothed; gray bark has sharply raised bumps & ridges

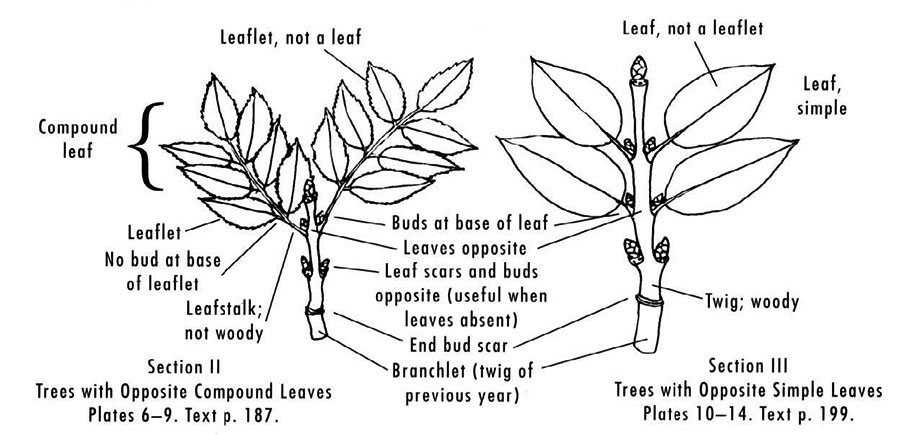
Pinnately Compound Leaves (alternate except for ash)
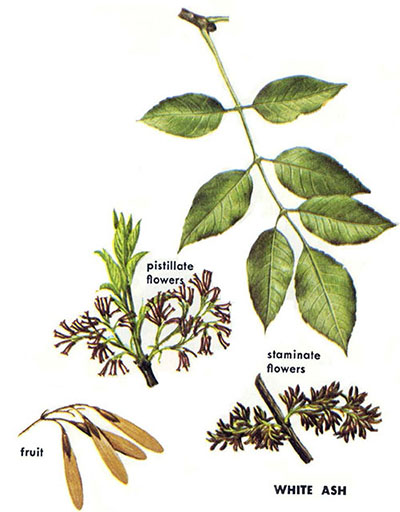
FA: White Ash (Fraxinus americana): opposite leaves, 5-9 leaflets untoothed or rounded teeth; fissured gray bark; small dark flattened bud
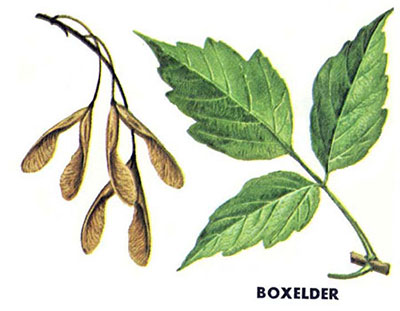
AN: Boxelder (Acer negundo): 3-5 notched leaflets; poison ivy-like; rough light brown bark
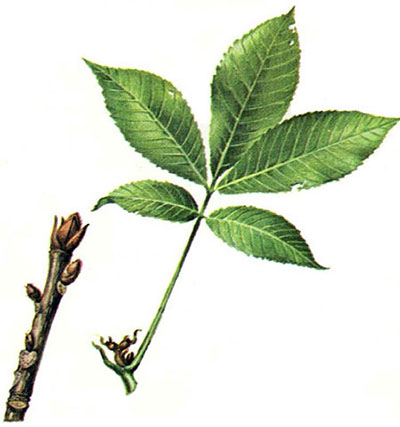
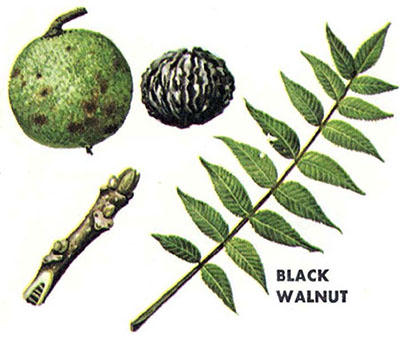
JN: Black Walnut (Juglans nigra): 7-17 leaflets (most); thick furrowed rough brown bark
Hickories: alternate leaves; 5-11 leaflets sharply toothed
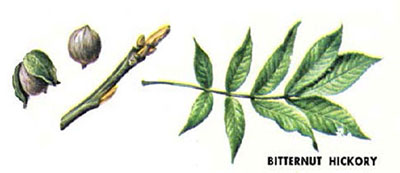
CA: Bitternut (Carya cordiformis): 7-11 leaflets; smooth ridged bark; "candleflame" bud; thin yellowish pointed fruit husk
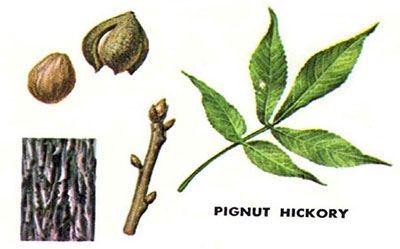
CG: Pignut (Carya glabra): 5-7 leaflets, smooth; ridged diamond pattern bark; bud small, oval; fruit narrow at base, husk smooth, dark
CO: Shagbark (Carya ovata): 5 leaflets, hairy below on primary vein; distal leaflets larger bark gray, hard loose plates; large oval hairy dark bud; thick ridged husk
